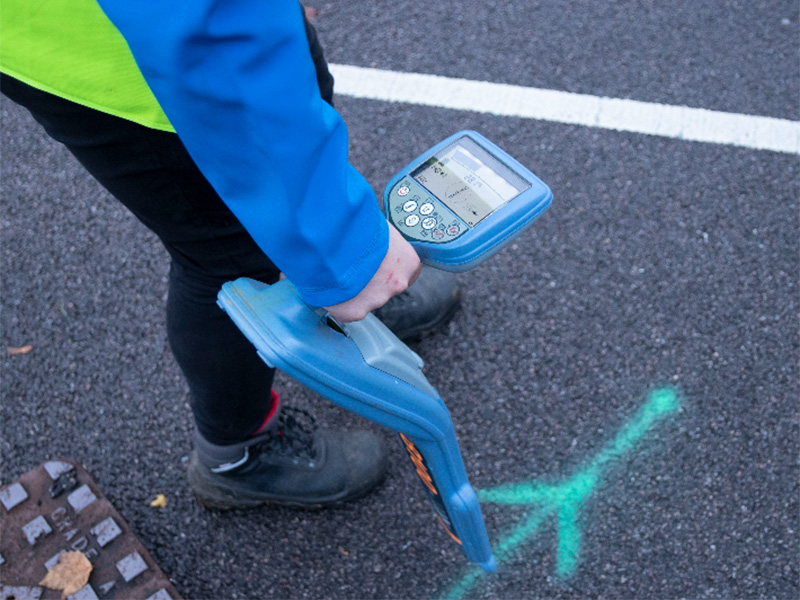
An underground utility survey is a crucial process used to identify and accurately map the location of buried utilities and infrastructure. Using specialist equipment, trained surveyors can detect underground features that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye.
To achieve reliable results, these surveys must be conducted by experienced professionals. It takes years to develop the expertise needed to interpret utility layouts correctly and account for site-specific variables that can affect signal detection and data accuracy.
It is important to ensure you hire a competent survey company, as a poor-quality survey can lead to major project delays, unexpected costs, and safety hazards.
The Importance of Mapping Underground Utilities
Accurate mapping of underground utilities is essential for construction, renovation, and excavation projects. The primary objective of an underground utility survey is to mitigate the risk of striking buried services when breaking ground.
Why This Matters:
- Avoiding costly mistakes – Accidental utility strikes can delay projects and incur significant financial penalties.
- Enhancing safety – Damaging underground infrastructure can lead to injuries and, in severe cases, even fatalities.
- Ensuring compliance – Many regulations require contractors to conduct a thorough utility survey before any excavation.
- Improving planning – The geospatial data obtained in the survey is invaluable for designing how new developments will connect to existing utility networks.
By identifying and mapping utilities before work begins, project managers can plan effectively and prevent unexpected disruptions.
What is an Underground Utility Survey?
An underground utility survey is a process used to locate and map buried services with high precision. This is achieved using a combination of advanced detection technologies that allow surveyors to identify different types of infrastructure, including water, gas, electricity, telecoms, and drainage systems.
Methods Used in Underground Utility Surveys
Two primary methods are employed to detect and map underground utilities:
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
GPR is a geophysical technique that transmits high-frequency radio waves into the ground. When these waves encounter a change in material—such as pipes, voids, or underground structures—they reflect back to the surface, allowing surveyors to map their position and depth.
Advantages of GPR:
- Can detect both metallic and non-metallic utilities.
- Provides depth information for underground features.
- Effective for identifying voids and underground storage tanks.
Limitations of GPR:
- Performance depends on soil type—clay-rich soils can reduce accuracy.
- Highly dependent on utility size and depth—smaller and deeper pipes may be harder to detect.
Electromagnetic Locating (EML)
EML works by transmitting electromagnetic signals along conductive underground utilities. A receiver at the surface detects these signals, allowing surveyors to determine the location, depth, and type of service.
How EML Works:
- Active Detection – A frequency is applied to a known service, which is then traced from the surface.
- Passive Detection – Naturally occurring signals from live electricity cables and metallic pipes are detected without needing direct access.
Limitations of EML:
- Cannot detect non-metallic utilities such as plastic water pipes unless a sonde (a signal-emitting device) is inserted.
- Accuracy depends on signal strength and interference from nearby utilities.
Why Both Methods Are Used Together
Because each method has its own strengths and limitations, they are always used in conjunction to ensure a complete and reliable survey. GPR is particularly useful for detecting non-metallic services, while EML is effective for tracing conductive utilities.
Utility Mapping Software & Data Processing
Once survey data is collected, it is processed using specialist mapping software. This post-processing stage enhances accuracy by allowing surveyors to:
- Interpret GPR data more effectively by filtering out noise.
- Overlay survey results onto existing site plans or topographical surveys.
- Generate clear, detailed utility maps for contractors and planners.
Utility maps provide essential geospatial data that ensures projects can proceed safely and efficiently while minimising the risk of utility strikes.
What Services Can Be Identified with an Underground Utility Survey?
An underground utility survey can detect a wide range of buried infrastructure, helping project managers and contractors make informed decisions before breaking ground. The ability to locate these utilities depends on the method used, the material of the service, and site conditions.
Services That Can Be Identified Using Electromagnetic Locating (EML)
- Metallic gas and water mains of 38mm diameter and greater
- Electricity supply cables from 440v to 66kV that are live
- Electric cables supplying street lighting
- Drainage runs of 100mm diameter or greater, where access allows
- Telephone, communications, and data cables
- Empty ducts of 100mm or greater
- Underground heating pipes
- Metallic pumping mains
- Other metallic services capable of carrying a detectable signal
Services That Cannot Be Located Using EML But May Be Detectable with GPR
- Plastic gas and water mains over 38mm in diameter
- Underground storage tanks
- Voids beneath the surface
- Empty ducts
- Non-metallic infrastructure over 38mm in diameter
Services That Are Unlikely to Be Identified by Either EML or GPR
- Non-metallic gas and water mains smaller than 38mm
- Pot-ended cables
- Fibre optic cables with no conductive element
- Disused services
Each underground site presents different challenges, and surveyors will use a combination of techniques to achieve the best possible detection results.
What Is a Desktop Utility Search and Why Is It Needed?
A desktop utility search is an essential part of an underground utility survey. It compiles existing records from utility providers, offering insight into what infrastructure is expected to be present in a specific area. This search can be conducted as part of a full utility survey or as a standalone service.
Why Is a Desktop Utility Search Important?
- Prepares surveyors before arriving on-site – Knowing what to expect helps plan the survey efficiently.
- Identifies key utilities that may be difficult to detect – Some non-metallic or smaller services may not be locatable through standard survey methods.
- Reduces project risks – Awareness of underground utilities helps avoid unnecessary excavation near sensitive infrastructure.
However, it is important to note that desktop utility records should only be treated as indicative and not as exact representations of buried services. Many records may be outdated, incomplete, or missing private utility installations.
Why a Combined Approach Works Best
For the most accurate understanding of underground infrastructure, both a desktop utility search and a physical underground utility survey should be conducted. This is particularly important for PAS128-compliant surveys, where gathering the most comprehensive data is mandatory.
A desktop utility record search can also include:
- Independent utility providers with local networks
- UXO (Unexploded Ordnance) searches for areas with historical military activity
By combining existing records with on-site survey methods, surveyors can piece together the full picture of underground utilities, improving safety and planning efficiency.
Ensuring Accurate Data for Planning and Design
Accurate utility mapping is essential when planning construction, infrastructure upgrades, or property development. For example, when installing a new drainage system, it is vital to know where the existing foul and surface water drainage systems are located. This ensures that new connections align with government guidelines and regulations.
A professional utility survey provides data on:
- The exact locations of manholes, pipe sizes, and flow directions
- Utility connections that need to be incorporated into the new design
- Potential obstacles that could affect construction
Having this level of detail enables project managers and engineers to design and implement new infrastructure with confidence, avoiding costly errors.
How Does an Underground Utility Survey Work?
A step-by-step process is followed to ensure accurate and reliable data collection.
1. Initial Site Assessment and Planning
- The survey scope is defined, including the types of utilities to be located.
- A risk assessment is conducted to identify potential hazards.
- Any necessary permits are obtained before work begins.
2. Desktop Study and Data Collection
- Existing records from utility providers are gathered.
- The desktop utility search is reviewed to identify expected services.
3. On-Site Survey and Detection
- Manhole covers are lifted, and drainage networks are inspected.
- Sondes and drainage rods are used to trace non-metallic pipes.
- Electromagnetic locating (EML) is used to detect conductive utilities.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is deployed to detect non-metallic or deeper utilities.
4. Data Processing and Reporting
- Utility locations are recorded using GNSS and total station technology.
- Findings are processed using advanced mapping software.
- The final utility map and report are created, overlaying data onto a site plan.
By following this structured approach, surveyors ensure maximum accuracy and reliability in underground utility detection.
Why You Might Need an Underground Utility Survey
Construction Projects
- Avoiding accidental damage to underground utilities during excavation
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations
Infrastructure Maintenance
- Identifying faulty or damaged utilities
- Planning upgrades or repairs
Property Development
- Ensuring accurate site planning
- Avoiding costly project delays
Environmental Studies
- Understanding the impact of development on underground systems
- Avoiding disruption to natural watercourses and ecosystems
Benefits of an Underground Utility Survey
- Minimising risks and safety hazards associated with excavation
- Saving time and money by avoiding accidental utility damage
- Ensuring compliance with legal and environmental regulations
- Providing accurate data for long-term planning and asset management
Examples of When an Underground Utility Survey Is Essential
Residential Construction
A property developer planned to extend an existing property and add new buildings within the site boundary. A utility survey was essential to:
- Identify existing infrastructure
- Plan connections to existing services
- Prevent accidental damage to buried utilities
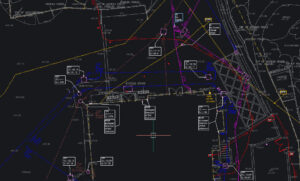
The underground utility survey was combined with a topographical survey, providing a comprehensive site overview to ensure smooth project execution.
Urban Development
A town centre roundabout was being redeveloped, requiring detailed knowledge of utility networks. A survey was undertaken to:
- Locate critical underground services
- Ensure construction work would not disrupt essential utilities
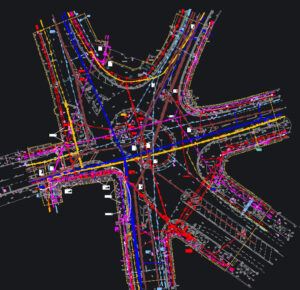
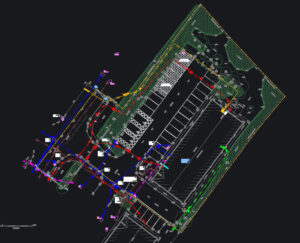
Industrial Sites
A busy industrial warehouse required new heavy machinery installation. A survey was needed to:
- Confirm no underground utilities would be impacted
- Plan for necessary modifications before construction began
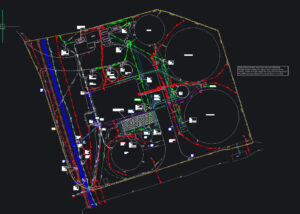
Public Infrastructure
A client sought to expand and improve their sewage waste system. An underground utility survey was essential for:
- Mapping existing infrastructure
- Identifying new connection points
Common Challenges in Utility Surveys
High-Density Urban Environments
Navigating built-up areas can be challenging due to restricted access and overlapping utility networks. In some cases, clearing overgrown vegetation may be required for accurate data collection.
Interference from Other Underground Materials
Survey signals can be disrupted by:
- Metal pipes and cables running close together
- Reinforced concrete (such as in pavements or roads)
- Nearby high-voltage power lines
Weather Conditions
- Wet ground conditions can affect GPR accuracy.
- Poor visibility on roadsides can create safety risks.
Choosing the Right Survey Provider
What to Look for in a Qualified Surveyor:
- Experience in similar projects – Underground utility surveys require years of training.
- Use of advanced equipment – Up-to-date technology improves accuracy.
- Proven track record – Reliable survey providers should have case studies demonstrating success.
There has been an increase in companies offering utility surveys without the necessary experience. Underground utility detection requires years of field experience, and even the most experienced surveyors continue to encounter new challenges. Choosing a reputable provider is crucial to obtaining accurate and reliable results.
Why Choose Terrain Surveys for Your Underground Utility Survey?
- Cutting-edge technology – High-precision equipment ensures detailed results.
- Extensive industry experience – Over 20 years in operation with a combined 50+ years of expertise.
- Diverse project experience – From power stations and sewage plants to residential developments and airports.
At Terrain Surveys, we are committed to delivering accurate, high-quality data that enables clients to make well-informed and safe decisions for their projects. Transparency, integrity, and professionalism are at the core of our service.
Contact Us
Get in touch with Terrain Surveys for a free site assessment and quote.
Visit our website or call today to discuss your project requirements.
